Order Types- Basic Explanation
In Forex, there are various types of orders that allow you to control your trades and manage your risk effectively. Here’s a basic overview of the most common types of orders:
Market Order: A “market order” is an instruction to buy or sell a currency pair at the current market price. It is executed immediately at the available price.
Pending Order: A “pending order” allows you to specify a price at which you want to enter a trade in the future. The two most common types of pending orders are:
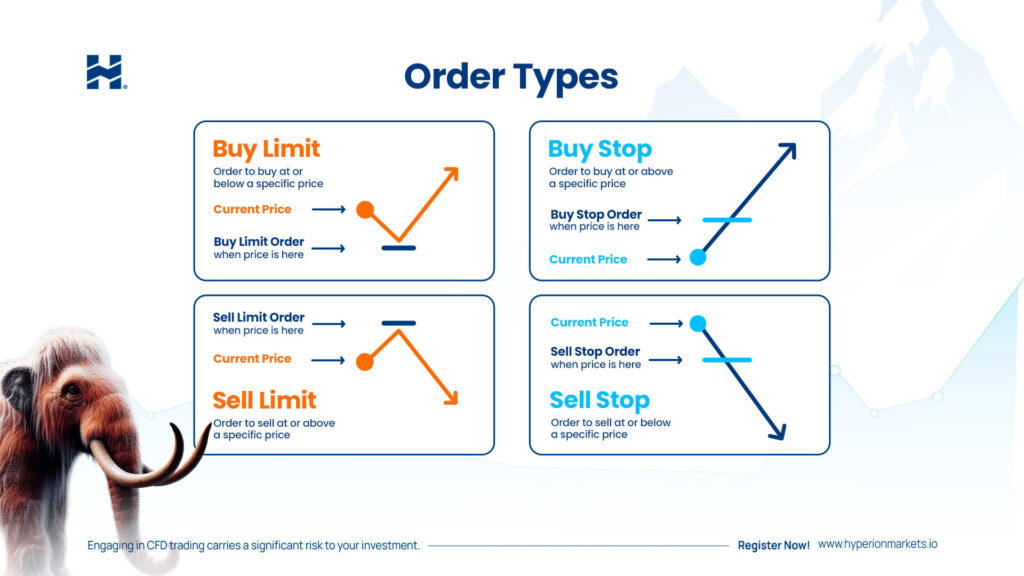
- Buy Limit Order: Executes if the price reaches or exceeds a specific level that is better than the current price.
- Sell Limit Order: Executes if the price falls to or equals a predetermined level that is better than the current price.
- Buy Stop Order: A buy stop order is placed above the current market price in anticipation that the price will continue to rise. Once the market price reaches or exceeds the stop price, the buy stop order is triggered, and a market order is executed to buy the asset at the prevailing market price.
- Sell Stop Order: A sell stop order is placed below the current market price, expecting the price to decline further. When the market price reaches or falls below the stop price, the sell stop order is activated, and a market order is executed to sell the asset at the prevailing market price.
Stop-Loss: A “stop-loss” is an order that defines a price level at which your trade will automatically close to limit losses if the market moves against you.
Take Profit: A “take profit” is an order that sets a price level at which your trade will automatically close to secure profits when the market moves in your favor.
Trailing Stop: A “trailing stop” is an order that automatically follows the price at a certain distance as the market moves in your favor. If the price reverses and touches the trailing stop level, the trade is closed to lock in profits.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Order Type
- Market Order:
- Functionality: Market orders execute at the current market price, useful for entering a trade immediately at the available price.
- Advantages: Quick execution, ensures immediate entry into the market.
- Disadvantages: May experience slippage (difference between desired price and actual execution price), which can impact costs.
- Pending Order:
- Functionality: Pending orders allow you to specify the price at which you want to enter a trade in the future.
- Advantages: Greater control over entry and exit points, useful for price-level-based strategies.
- Disadvantages: Does not guarantee execution if the market does not reach the specified level.
- Stop-Loss:
- Functionality: A stop-loss order automatically closes a trade if the price reaches a predefined level to limit losses.
- Advantages: Protects your capital by limiting losses, especially useful when you cannot constantly monitor the market.
- Disadvantages: May prematurely close trades if the price nears the stop-loss level and then reverses.
- Take Profit:
- Functionality: A take profit order automatically closes a trade when the price reaches a specific level to secure profits.
- Advantages: Secures profits without the need for constant market monitoring.
- Disadvantages: May close trades before they reach their maximum profit potential.
- Trailing Stop:
- Functionality: A trailing stop follows the price at a certain distance as the market moves in your favor, securing profits if the price reverses.
- Advantages: Allows you to capitalize on favorable market movements while protecting profits.
- Disadvantages: May close the trade if the market reverses before the trailing stop is triggered.
