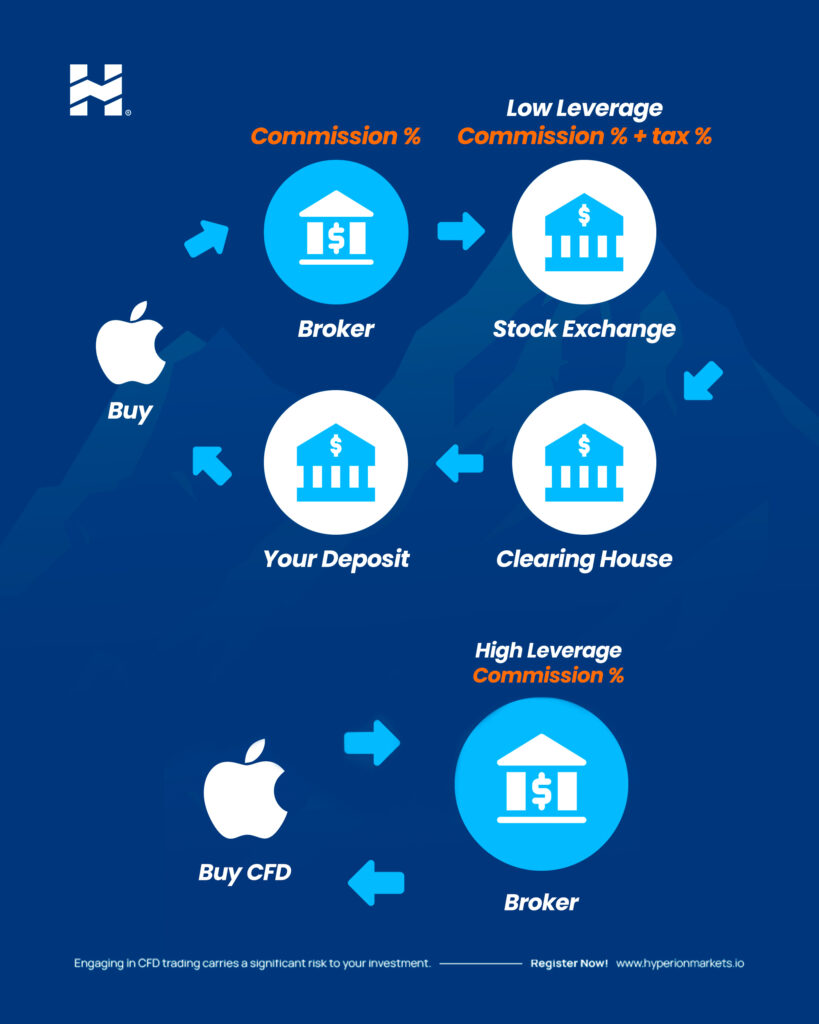
Introduction to Stocks CFDs
Trading in the stock market involves buying and selling financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, and others. Here’s a basic guide on how to trade in the stock market:
Education and Research: Before getting started, it’s essential to educate yourself on key stock market concepts. Familiarize yourself with terms like stocks, bonds, indices, and diversification. It’s also important to research companies and sectors you’re interested in.
Set Goals and Strategies: Define your investment goals and establish a strategy that aligns with those goals. Decide whether you’re interested in short-term trading or long-term investing.
Open an Account with a Broker: You’ll need to open an account to start trading in the stock market. There are online brokers that offer trading platforms and tools for making transactions.
Asset Research: Before purchasing any asset, conduct thorough research. Examine financial reports, perform technical and fundamental analysis, and follow news related to the assets you’re interested in.
Diversification: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversification reduces risk by spreading your investments across different asset classes and sectors.
Place Buy and Sell Orders: Once you’ve chosen the assets you want to invest in, you can place buy or sell orders through your broker’s platform. Orders can be market orders (at the current price) or limit orders (at a specific price).
Portfolio Tracking and Management: Regularly track your investments. Use portfolio tracking tools to assess the performance of your assets. Adjust your portfolio as needed based on your goals and market conditions.
Risk Management: Set loss limits and gain experience in risk management. Don’t invest more than you’re willing to lose, and consider using stop-loss orders to protect your investments.
Stay Informed: Stay abreast of economic news and events that may affect the markets. Macroeconomic events, earnings announcements, and geopolitical developments can have a significant impact on prices.
Learn from Experience: Practice and experience are crucial. Learn from your successes and failures, adjust your approach as needed, and continue educating yourself about financial markets.